Post Therapy Scans
Patient is a 57 -year-old female with history of pancreatic neuroendocrine cancer and distal pancreatectomy 12 yrs ago. She developed liver metastases and underwent liver transplant about 7 yrs ago. She has received multiple cycles of chemotherapy for metastatic abdominal lymphadenopathy and presents with progressive disease and multiple bilateral lung nodules.
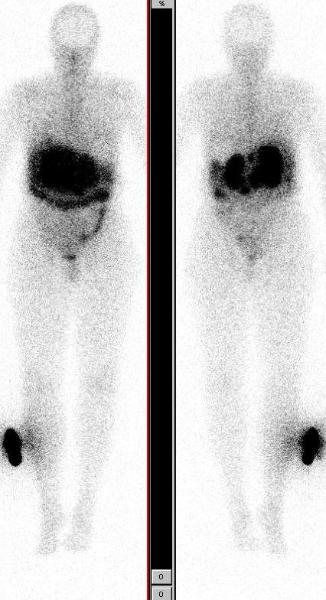
Images above show In-111 Octreotide scan in anterior and posterior projections, in dark and light intensities showing focal uptake in abdominal lymphadenopathy. She is asymptomatic, her Karnofsky performance score is 100 and the neuroendocrine markers not elevated.
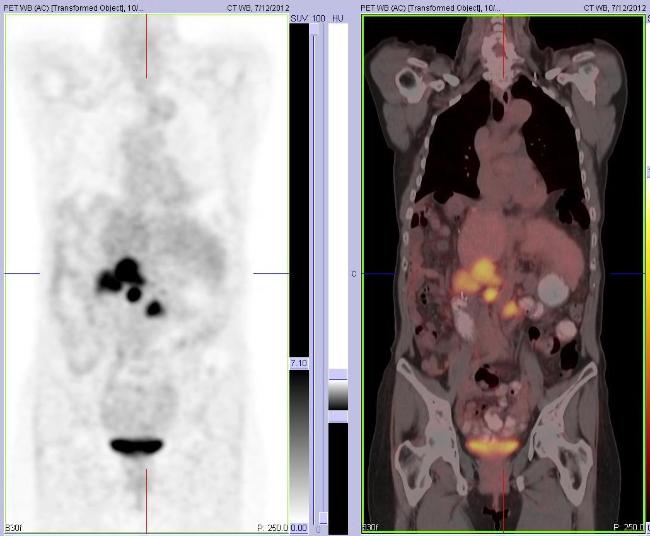
The whole body FDG PET/CT scan shows focal hypermetabolism in abdominal lymphadenopathy and mild uptake in bilateral lung nodules. She met the inclusion and exclusion criteria for investigational PRRT (Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy) with high dose In-111 Octreotide and was enrolled in the protocol.
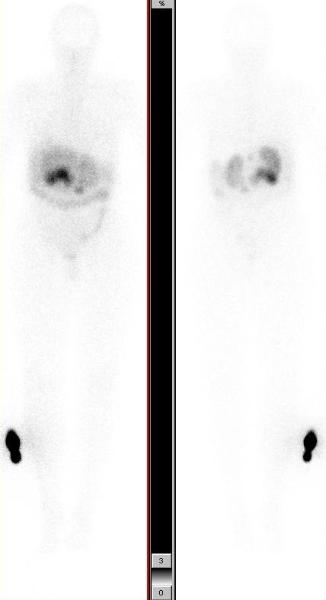
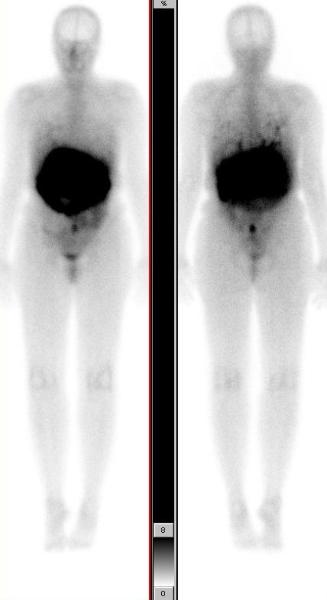
Images below show post therapy scans acquired 48 hrs after PRRT with 471.0 mCis of In-111 Octreotide. The anterior and posterior whole body scans are presented in two different intensities. They show good targeting with intense uptake in metastatic lymphadenopathy and uptake in bilateral lung nodules (scan shown in higher intensity).
This case illustrates the role of post therapy scan in confirming the metastatic etiology of bilateral lung nodules. These nodules did not show any uptake with the low dose of In-111 Octreotide used for diagnostic imaging, but were seen to take up In-111 Octreotide on the post therapy scan. This is likely due to higher radiopharmaceutical activity used for therapy, as compared to the diagnostic scan. This phenomenon is frequently seen in treatment of thyroid cancer patients with I-131, and comparing the I-131 post therapy scan with the diagnostic low dose I-131 scan.

Is detection of additional lesions in post-peptide receptor radionuclide therapy scans with respect to diagnostic imaging only due to different affinity of ligands?: a report of discordance between diagnostic and posttherapy imaging using the same ligand. Minutoli F, Herberg A, Sindoni A, Cardile D, Cucinotta M, Baldari S. Clin Nucl Med. 2012 Aug;37(8):817-8.