Category
Gnuc-com
Thyroglossal Duct Remnant
A 63 year old male who was found to have papillary thyroid cancer on the FNA of a cold thyroid nodule, presented post thyroidectomy for remnant ablation. Pre-treatment I-131 scan showed focal uptake in the thyroid bed consistent with thyroid remnant and a focus of uptake superior to the thyroid remnant in the midline neck.
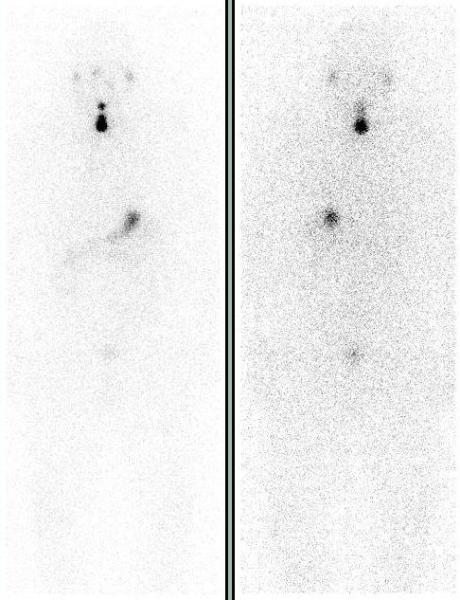
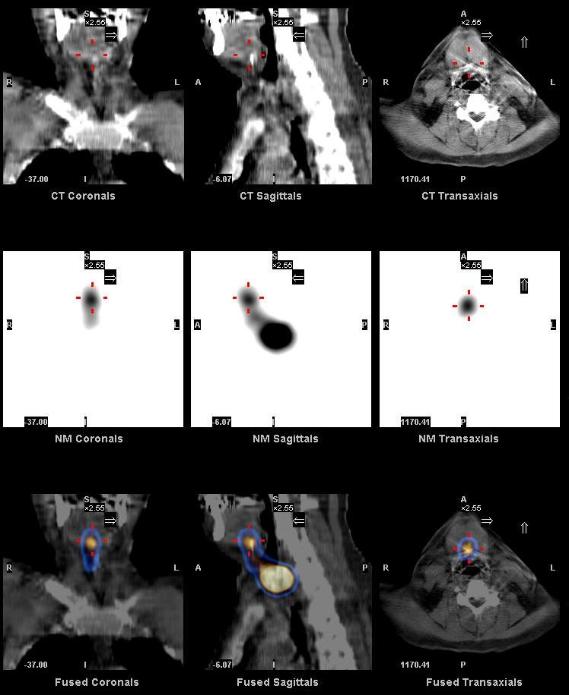
SPECT-CT localized this focus of uptake to the base of the tongue, in the region of foramen cecum, consistent with a thyroglossal duct remnant.
Remnant ablation was preformed with 100 mCi of I-131 and was well tolerated.
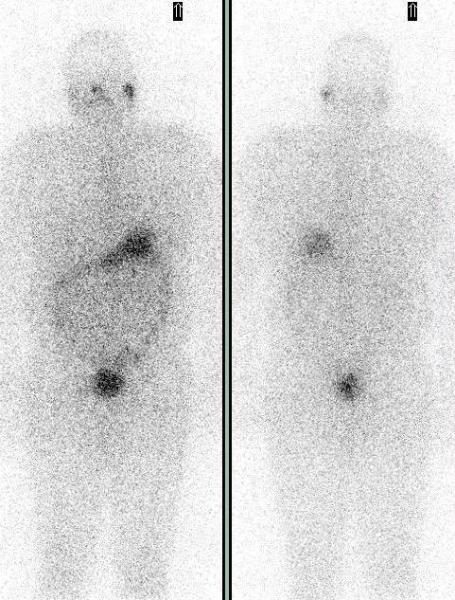
A one year follow up I-131 whole body scan showed the resolution of the thyroid remnant and thyroglossal duct remnant.
1. Zanotti-Fregonara P, Hindié E, Keller I, Calzada-Nocaudie M, Devaux JY. Scintigraphic visualization of glossal thyroid tissue during the follow-up of thyroid cancer patients. Clin Nucl Med. 2007 Dec;32(12):911-4.
2. Rao PN, Pandit N, Kumar R, Upadhya IV, Vidya Sagar MS. Ectopic functioning thyroid tissue in the thyroglossal duct detected by radionuclide imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2005 Sep;30(9):630.
This case was compiled by Dr. David He, BCM
Metastatic Carotid Body Tumor
The patient is a 78 year old man with a history of a left neck glomus tumor diagnosed about 10 yrs ago, presented with complaints of worsening left thigh pain. X-ray showed a 2.4 cm lytic lesion in proximal left femur. CT-guided biopsy demonstrated metastatic neuroendocrine tumor.
A whole body FDG PET-CT showed intense focal hypermetabolism (SUV max 26) in the large left neck mass extending from the base of the skull to the superior aspect of the hyoid bone, invading the left petrous temporal bone, and encasing the internal carotid artery and jugular vein. Hypermetabolism was also seen in left level IIb lymph nodes (SUV max 9.5), a 1.4 cm nodule in the right lung base (SUV max 6.4), and a lytic lesion in the left proximal femur (SUV max 18.0).
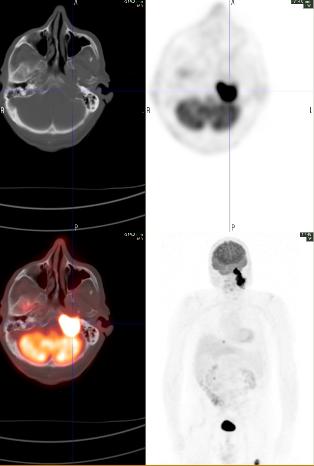
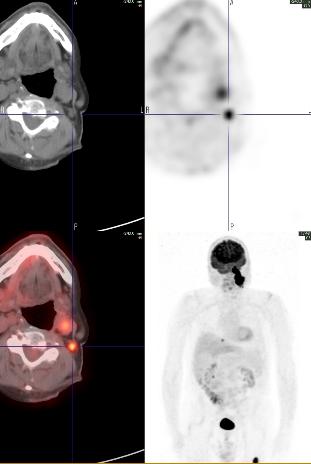
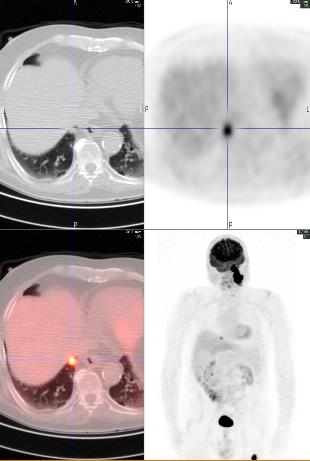
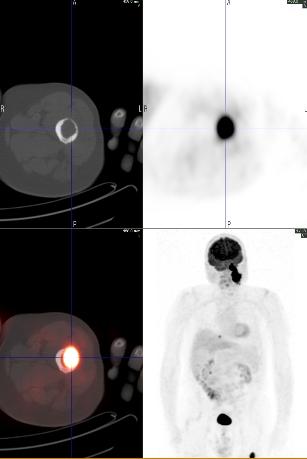
A subsequent In-111 Octreotide scan showed increased tracer uptake in the left neck mass and femur, but not in the cervical lymph nodes or lung nodule.
More metastatic lesions were seen on the FDG PET-CT compared to the Octreotide SPECT-CT. In the interim patient also had open reduction and internal fixation at the left femur.
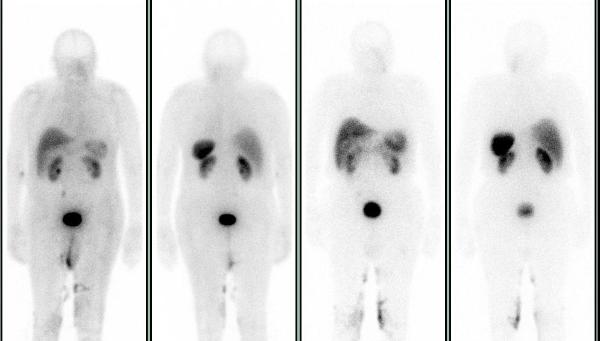
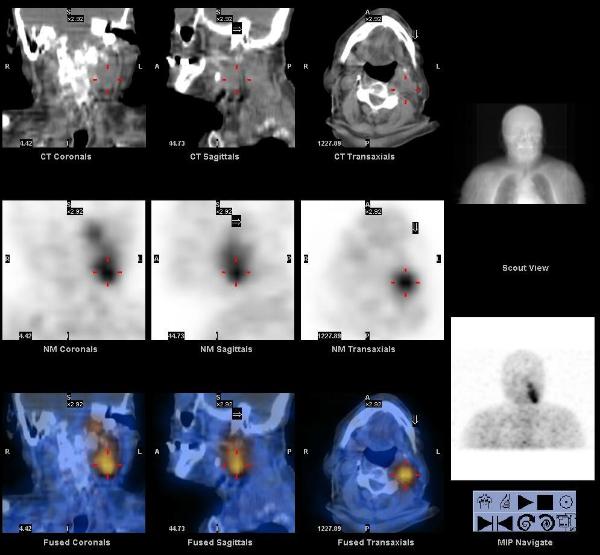
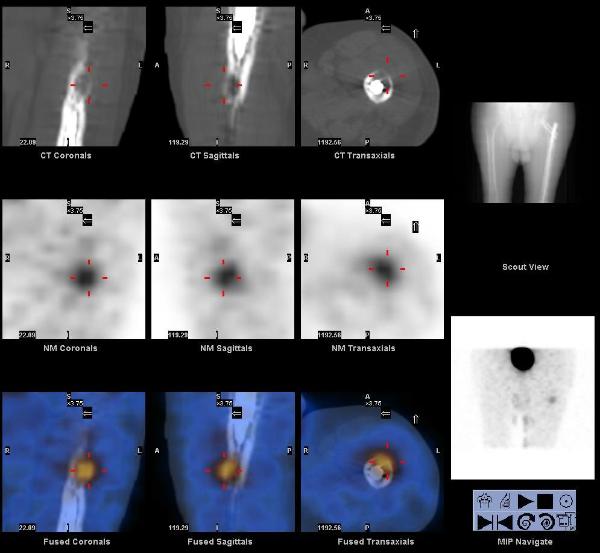
Carotid body tumors are paragangliomas (extra-adrenal pheochromocytomas) arising from the carotid body. They arise close to or envelop the bifurcation of common carotid artery, usually in the sixth decade of life, and may be familial with autosomal dominant transmission in MEN 2 syndrome. They frequently recur after resection, many metastasize, and 50% ultimately prove fatal by direct invasion.
1. FDG PET imaging of paragangliomas of the neck: comparison with MIBG SPET. Macfarlane DJ, Shulkin BL, Murphy K, Wolf GT. Eur J Nucl Med. 1995 Nov;22(11):1347-50.
2. PET scan assessment of chemotherapy response in metastatic paraganglioma. Argiris A, Mellott A, Spies S. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003 Dec;26(6):563-6.
This case was compiled by Dr. Matthew R. Galfione, BCM
Recurrent Paraganglioma
A 65 yrs old male was found to have extremely high blood pressure during work up for pacemaker placement. Subsequent biochemical studies revealed elevated urine and plasma cathecolamine metabolites. Patient has past medical history of right sided retroperitoneal paraganglioma resected 23 years ago.
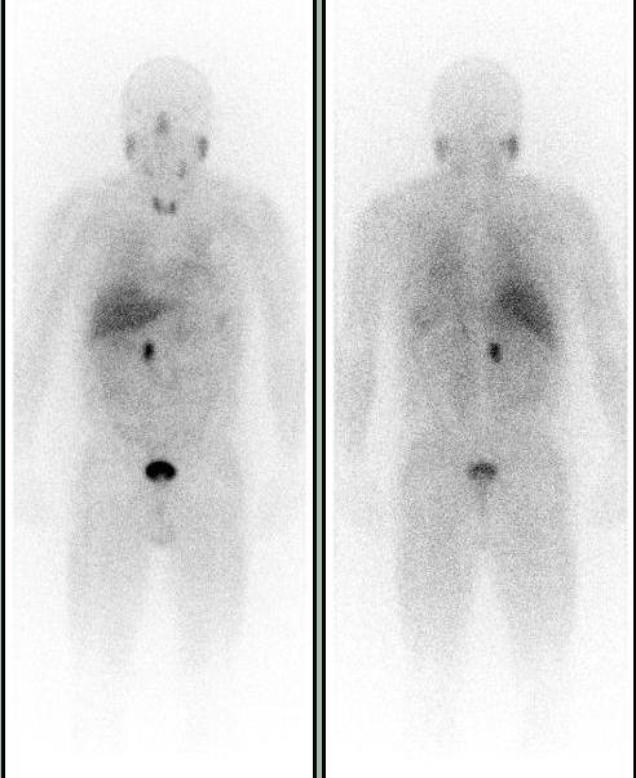
Suspected to have a recurrent paraganglioma or new pheochromocytoma, patient was referred for an MIBG scan to localize the tumor and possible metastasis. Whole body images show focal abnormal uptake in the right paramedian midabdomen.
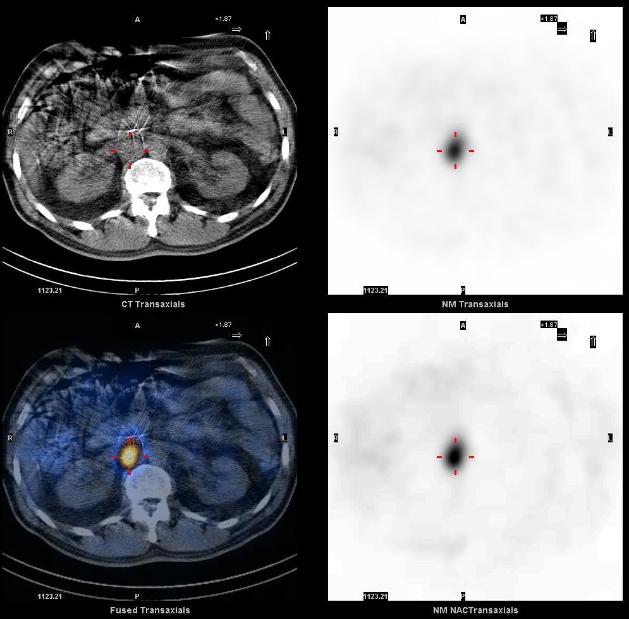
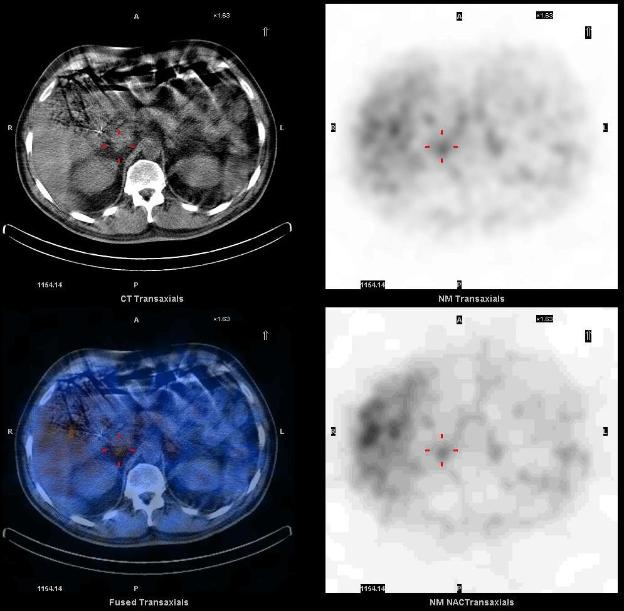
I-123 MIBG SPECT-CT demonstrates a focus of markedly increased uptake in the abdomen, corresponding to a soft tissue mass in the right retroperitoneal paracaval region just superior to the right renal vessels. Mild physiologic uptake is seen in the normal adrenals. The tumor and the right adrenal gland were surgically removed without complications. Pathology identified malignant paraganglioma in the tumor and the normal adrenal. MIBG SPECT-CT helped localize recurrent paraganglioma for surgical resection.
1. Detection and treatment of pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas: current standing of MIBG scintigraphy and future role of PET imaging. Havekes B, Lai EW, Corssmit EP, Romijn JA, Timmers HJ, Pacak K. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008 Dec;52(4):419-29.
2. Scintigraphic imaging of body neuroendocrine tumors. Intenzo CM, Jabbour S, Lin HC, Miller JL, Kim SM, Capuzzi DM, Mitchell EP. Radiographics. 2007 Sep-Oct;27(5):1355-69.
This case was compiled by Dr. David He, BCM
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
A 47 years old Caucasian male with a history of metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma (diagnosed 2 years ago when he presented with obstructive uropathy and elevated PSA, had retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy and Gleason score of 5+5=10, highest grade, was treated with chemotherapy and androgen blockade with good response) presented with rising PSA (increase from 0.1 to 10.1 ng/ml), despite radiographic improvement in the prostate on recent CT and a negative whole body bone scan.
Currently, no urinary or GI complaints.
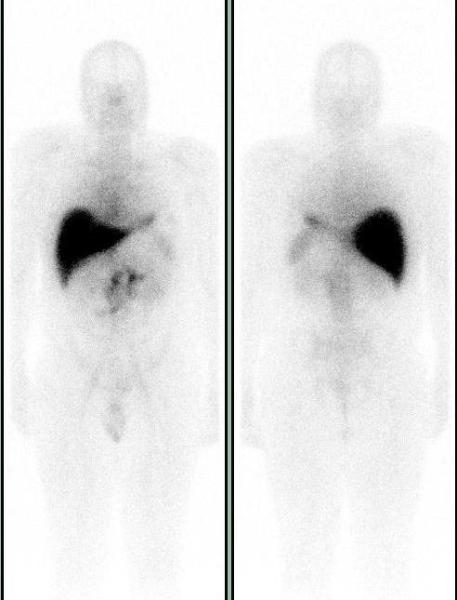
A Prostascint study was ordered to determine the cause of the rising PSA. Five days after the injection of 7.0 mCi of In-111 Capromab pendetide (prostascint – Indium labeled monoclonal antibody that reacts with (PSMA) prostate specific membrane antigen) whole body images were acquired in anterior and posterior projections and SPECT-CT images of the abdomen and pelvis were acquired. Unlike PSA, PSMA is a membrane glycoprotein that correlates with the aggressiveness of malignancy. It is expressed in all prostate tissue, malignant and benign. The conjugated antibody also binds duodenal epithelial cells and proximal tubule cells in the kidney.
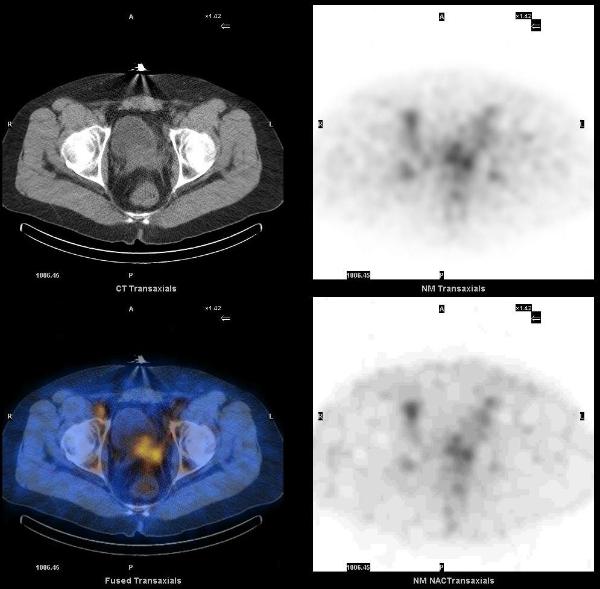
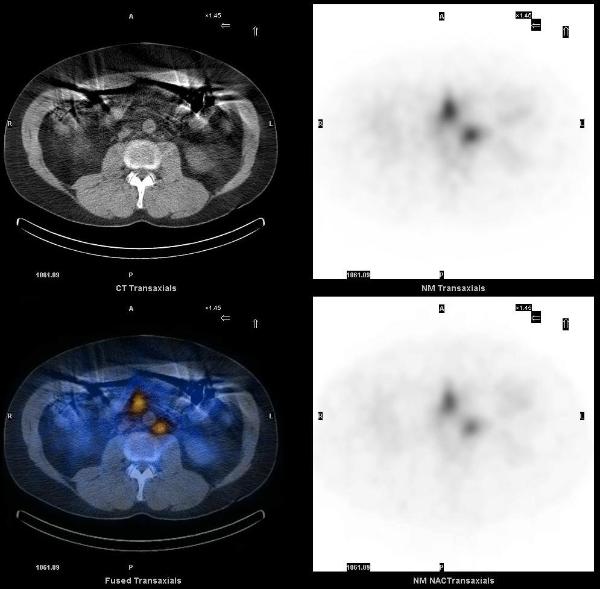
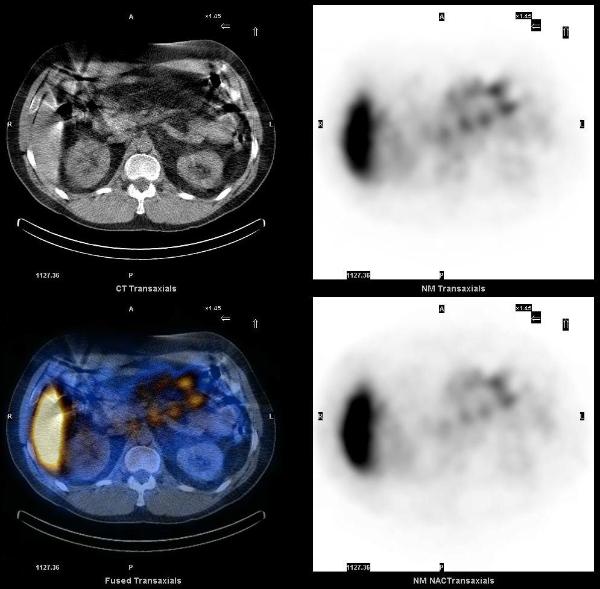
On SPECT-CT images, ProstaScint uptake is noted in prostate gland and in several retroperitoneal lymph nodes, particularly in the left para-aortic region. There are also foci of increased uptake in the central abdomen and left upper quadrant, which correspond to mesenteric lymph nodes.
1. Manyak MJ. Indium-111 capromab pendetide in the management of recurrent prostate cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008 Feb;8(2):175-81.
2. Chang, SS. Overview of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen. Rev Urol. 2004; 6 (Suppl 10): S13–S18.
This case was compiled by Dr. Vivek Bansal, BCM
Metastatic Rectal Carcinoid
A 65 years old asymptomatic male who tested positive for fecal occult blood testing was found to have a rectal mass on colonoscopy, initially reported as an adenocarcinoma. Staging workup included a CT scan of the abdomen which showed a neoplasm in the liver, with neuroendocrine features on fine needle aspiration.
Planar 24 hr whole body In-111 octreotide scan images showed a small focus of mild uptake in lateral left lower chest, a large focus of intense uptake in the liver, and four distinct foci of mild to moderately increased uptake in the lower abdomen and pelvis.
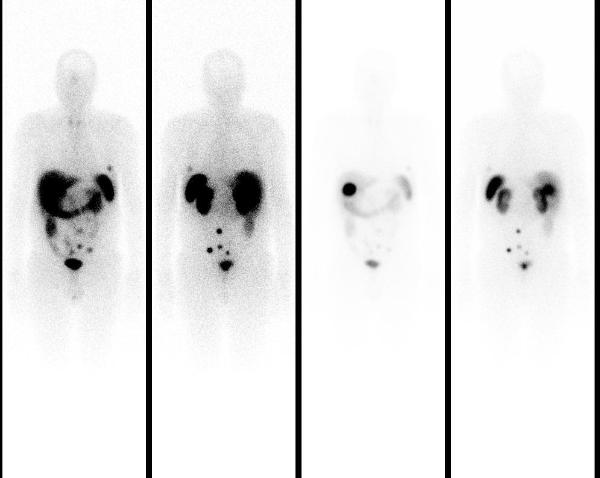
SPECT-CT images localized these abnormalities to: focal uptake in the rectal wall thickening, two presacral soft tissue nodules, the liver mass, and multiple bone metastasis (left ilum, L5 pedicle, and the left 6th rib).
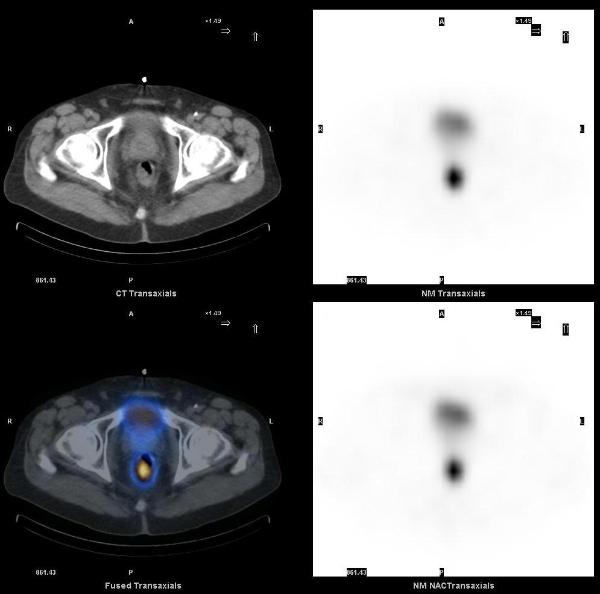
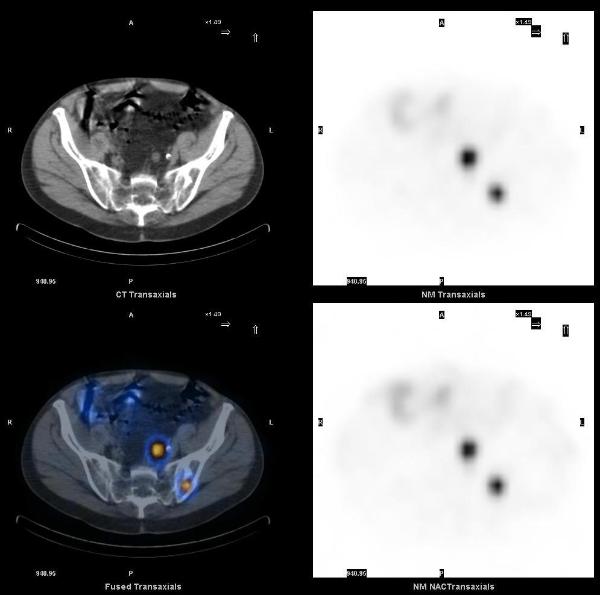
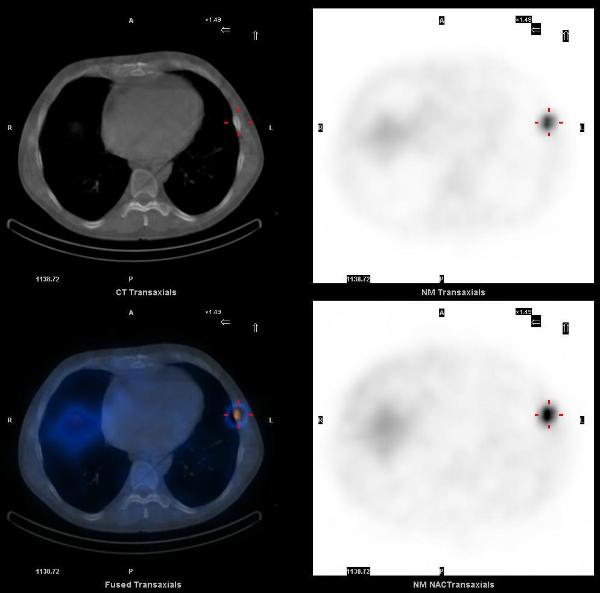
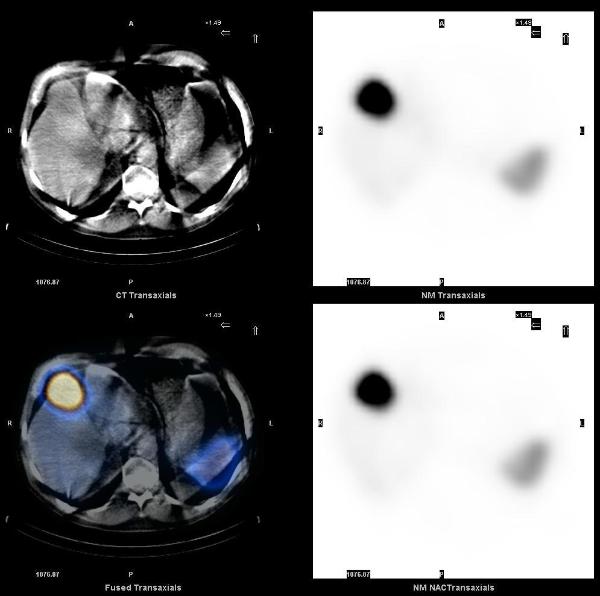
The overall incidence of carcinoid tumor is increasing, partly due to improvements in diagnostic imaging. The best modalities for diagnosis and staging of carcinoids are In-111 Octreotide, I-123 MIBG and F-18 FDG PET-CT. SPECT-CT imaging helps in accurate localization of abnormal uptake seen on planar scintigraphy. Rectum is the third most common site of gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors. Rectal carcinoids are usually asymptomatic, carcinoid syndrome does not occur in these patients, and the incidence of metastases is low.
1. Anatomic and functional imaging of metastatic carcinoid tumors. Scarsbrook AF, Ganeshan A, Statham J, Thakker RV, Weaver A, Talbot D, Boardman P, Bradley KM, Gleeson FV, Phillips RR. Radiographics. 2007 Mar-Apr;27(2):455-77.
2. A proposed staging system for rectal carcinoid tumors based on an analysis of 4701 patients. Landry CS, Brock G, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM, Martin RC 2nd. Surgery. 2008 Sep;144(3):460-6.
This case was compiled by Dr. Sabeen Rahman, BCM
Hepatic Hemangioma
60 yrs old male presented with a 3.2 x 2.8 cm indeterminate liver mass seen in the right lobe, on the CT scan. Subsequent MRI study found characteristics atypical for a hemangioma.
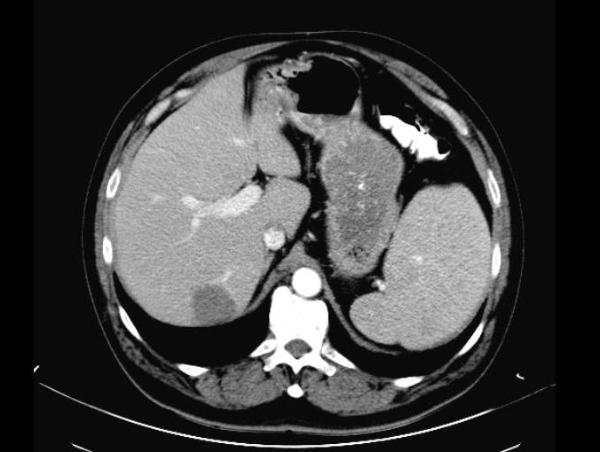
Tc-99m labeled RBC scan showed a focus of increasing uptake on the dynamic images (posterior projection), and focal intense uptake corresponding to the liver mass, on the SPECT-CT, characteristic of hemangioma.
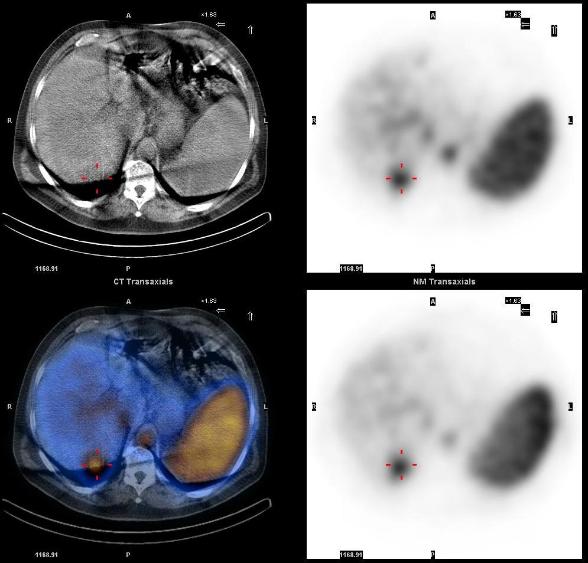
1. Review of hepatic imaging and a problem-oriented approach to liver masses. Bennett WF, Bova JG., Hepatology. 1990 Oct;12, 761-75
This case was compiled by Dr. David He, BCM
Splenosis on SPECT-CT
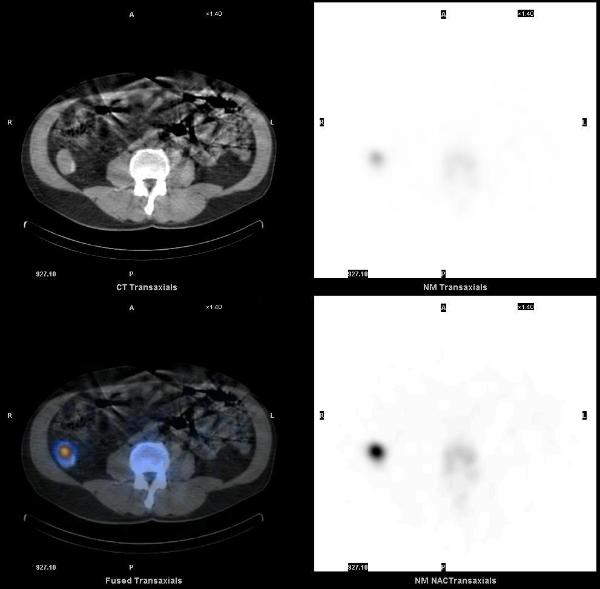
A 60 yrs old male, smoker, with a past medical history of hypertension, and remote h/o post trauma splenectomy presented with symptoms of UTI. He was found to have microscopic hematuria which did not resolve with antibiotics and a CT scan of the abdomen was performed. It showed multiple enhancing soft tissue density masses in the abdomen and pelvis.
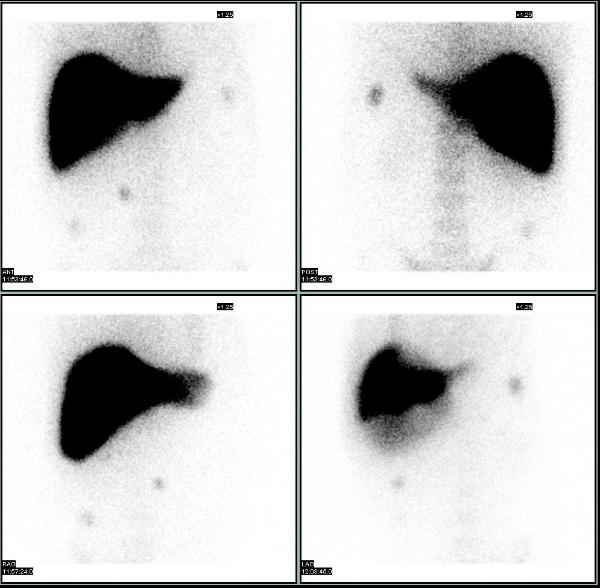
Splenosis was suspected and a liver-spleen scan was acquired after the injection of 8.7 mCi of Tc-99m sulfur colloid. Planar images showed multiple scattered foci of increased uptake in the abdomen and pelvis, consistent with splenosis. SPECT-CT images showed that all the enhancing lesions seen on the diagnostic CT corresponded to foci of increased uptake, consistent with splenic tissue.
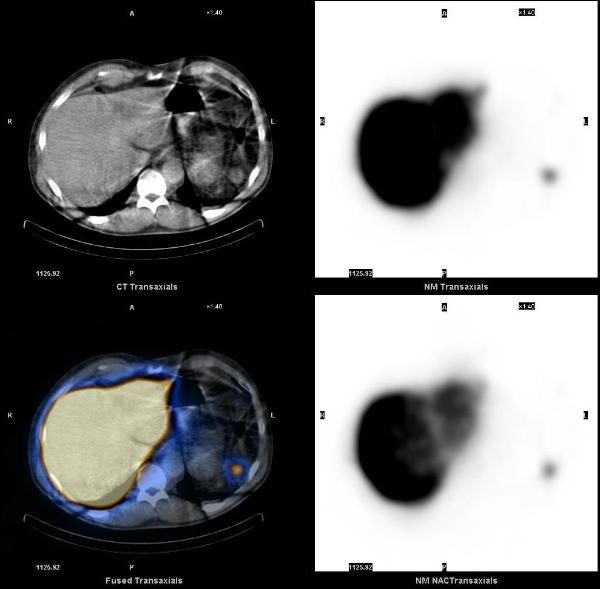
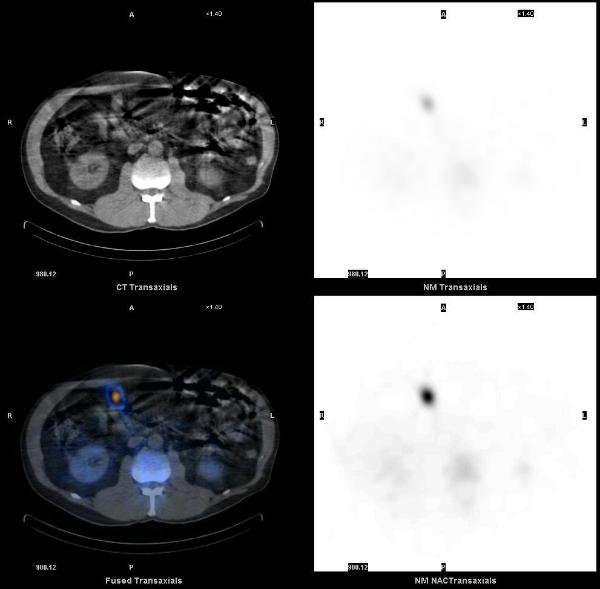
1. Splenosis: 99mTc-labelled colloids provide the diagnosis in splenectomised patients. Franceschetto A, Casolo A, Cucca M, Bagni B. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006 Sep;33(9):1102.
2. Splenosis presenting as multiple intra-abdominal masses mimicking malignancy.Kok J, Lin M, Lin P, Ngu C, Sam S, Loh C, Kociuba K. ANZ J Surg. 2008 May;78(5):406-7.
This case was compiled by Dr. Joji Varghese, MEDVAMC
Cholecysto-colonic Fistula
72yrs old male was referred for hepatobiliary scintigraphy because of complaints of right upper quadrant abdominal pain, made worse by defecation. Dynamic 1 min/ frame images of the abdomen were acquired in anterior projection after intravenous administration of 6.7 mCi of Tc-99m labeled mebrofenin (Choletec).
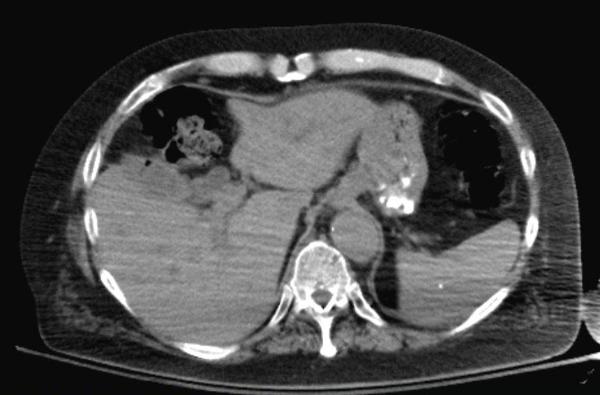
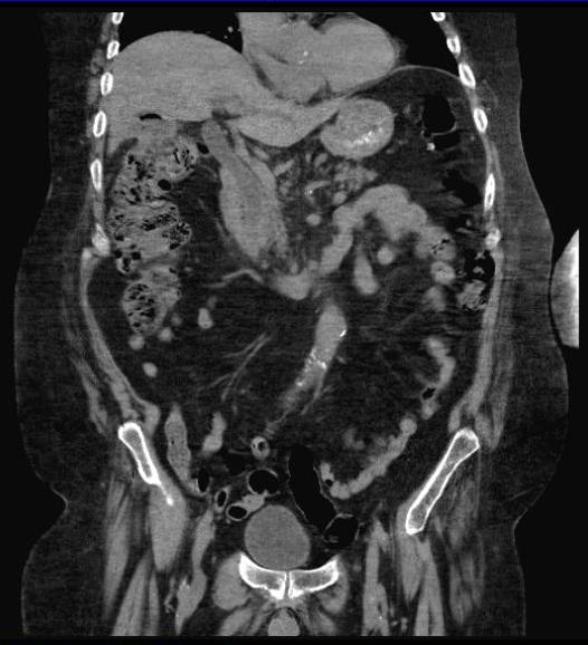
The images show good uptake by the liver suggesting adequate hepatocellular function. Activity is seen entering the common bile duct and the gall bladder, excluding cystic duct obstruction/ acute cholecystitis. Towards the end of 1 hr of imaging, the gall bladder activity is seen to move in the pattern of transverse colon and abrupt cutoff is seen in the common bile duct, without any small bowel activity. These findings suggest cholecysto-colonic fistula and partial common bile duct obstruction.
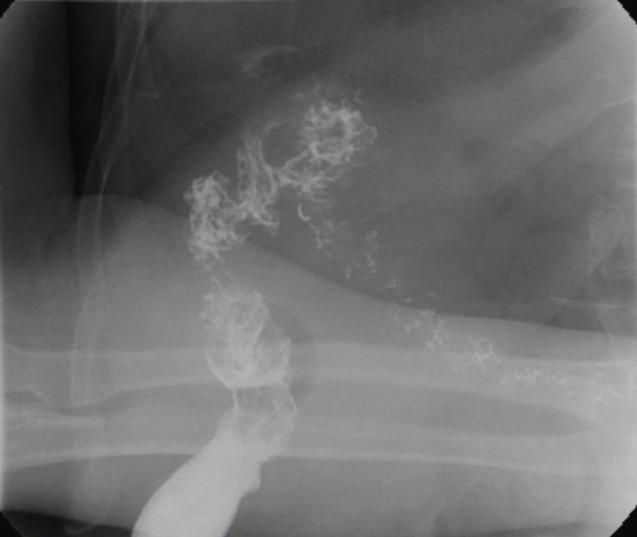
Cholecysto-colonic fistula was confirmed on barium enema. Supporting findings seen on the CT scan included the presence of air in the gall bladder and loss of fat plane between the gall bladder and the hepatic flexure of colon. Sphinterotomy was done on the follow up ERCP and multiple large stones were removed from the CBD.
This case was compiled by Dr. David He, BCM